The myths about lithium batteries: truths and misconceptions debunked
Lithium batteries have become an essential part of our daily lives, powering smartphones, laptops, electric cars, and even renewable energy storage systems. However, many misconceptions have arisen around this technology, often causing confusion and misinformation.
Let’s analyze the most common beliefs about lithium batteries and the scientific truths that debunk them.
1. Lithium batteries degrade rapidly
One of the most widespread myths is that lithium batteries have a very short lifespan. In reality, these batteries are designed to withstand thousands of charge-discharge cycles, maintaining significant capacity even after years of use. With proper charge management and controlled temperatures, degradation is very slow. On average, a lithium-ion battery can sustain between 500 and 3,500 cycles before reaching end-of-life, i.e. the point at which its capacity is significantly reduced.
2. Lithium batteries are dangerous and can explode
Another common misconception concerns the safety of lithium batteries. While improper use or manufacturing defects can cause overheating or malfunctions, modern Battery Management Systems (BMS) monitor temperature, voltage, and current to prevent issues. The risk of explosion is extremely low when using certified batteries and high-quality devices.
3. You need to fully discharge a battery before recharging it
This belief stems from older nickel-cadmium batteries but does not apply to lithium batteries. In fact, completely discharging a lithium battery can cause irreversible damage. It is preferable to maintain the charge between 20% and 80% to prolong its lifespan.
4. Lithium batteries fully discharge when not in use
Some people believe that an unused lithium battery will discharge completely over time. In reality, lithium batteries have a very slow natural discharge, especially when stored at an appropriate temperature. However, leaving them fully discharged for long periods can damage their internal chemistry, so it is recommended to store them with a charge level between 40% and 60%, recharging them monthly.
5. Lithium batteries do not perform well in cold temperatures
It is true that lithium battery performance can decrease in extremely low temperatures, but modern thermal management systems (such as integrated heating) mitigate this issue. Additionally, lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries are more tolerant to low temperatures compared to other lithium chemistries.
6. Lithium batteries pollute more than other technologies
Although lithium battery production requires significant energy resources, their environmental impact is lower compared to many alternatives, especially when considering their use in sustainable mobility and renewable energy storage. Moreover, lithium battery recycling is constantly evolving, and more companies are specializing in the recovery and reuse of valuable materials contained in battery cells.

Archimede Energia: innovation and reliability in lithium batteries
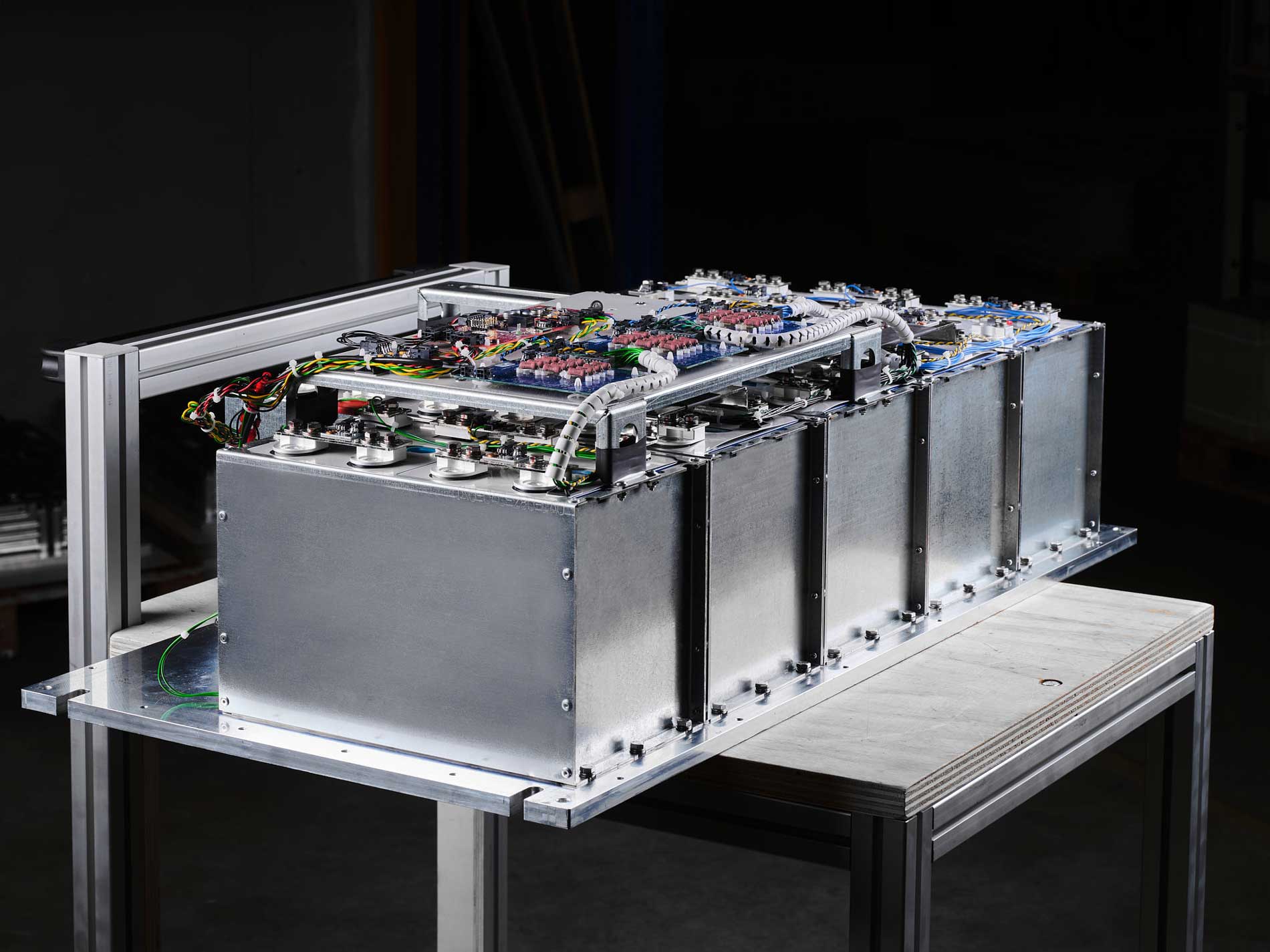
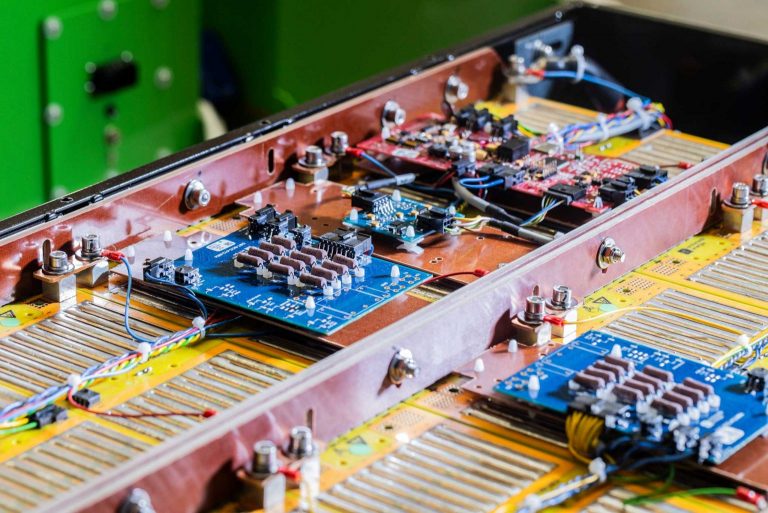
Archimede Energia is a specialized manufacturer dedicated to the development and production of high-quality lithium batteries. Through continuous research and innovation, we offer advanced solutions for sustainable mobility, energy storage, and industrial applications. Our batteries ensure high performance, safety, and longevity, meeting the needs of an ever-evolving market.
If you are interested in learning more about lithium batteries and their applications, stay connected with us. Contact us for more articles and updates!