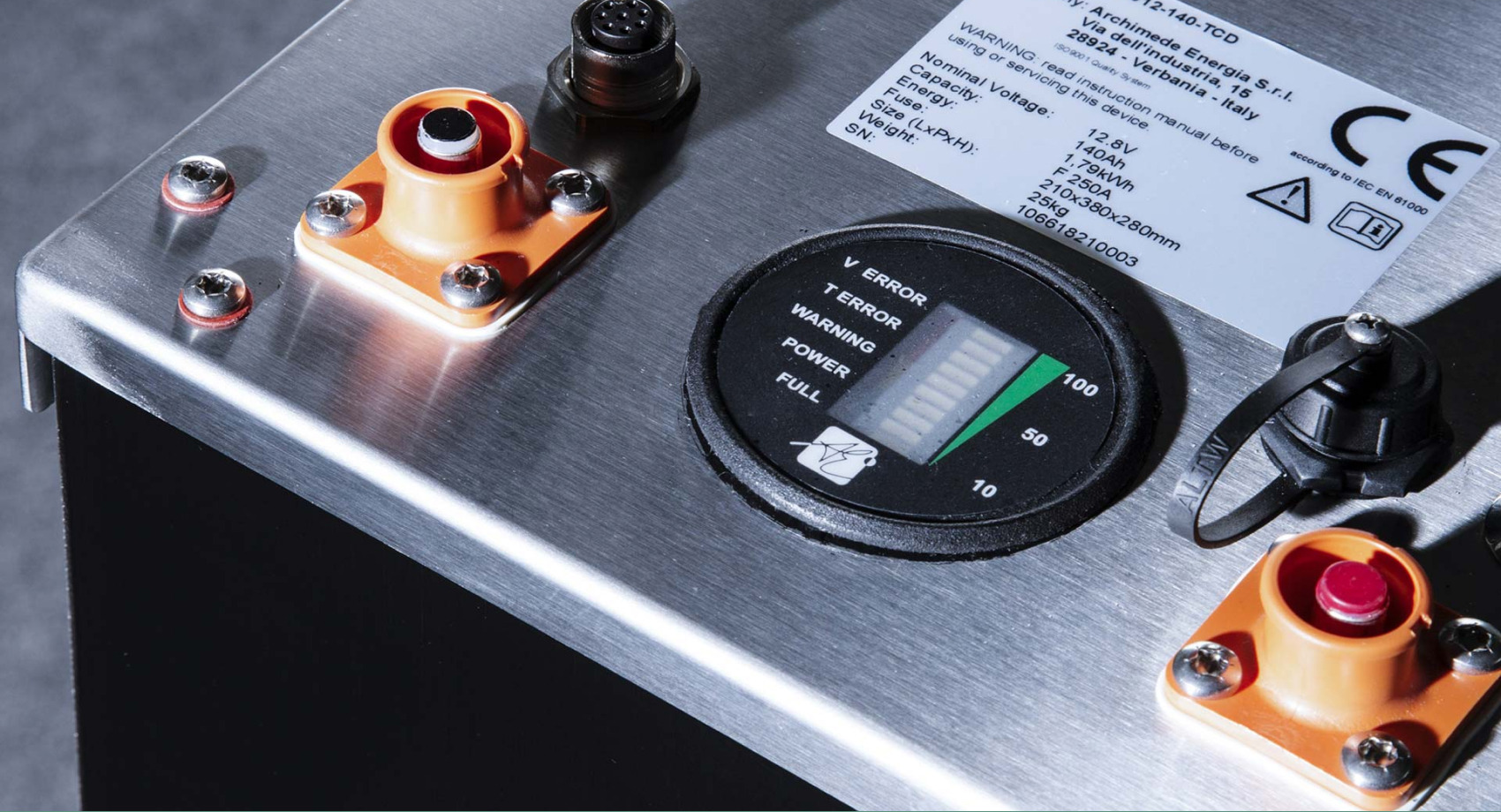
Archimede Energia Batteries are certified
Archimede Energia’s lithium batteries have obtained significant certifications, including Type Approval and ECE R100, which set them apart from the competition. This achievement demonstrates the company’s commitment to quality, safety, and regulatory compliance: key factors that customers can trust when choosing Archimede Energia’s energy storage solutions.
The approval process is a rigorous assessment conducted by authorized testing bodies. It ensures that a product meets the necessary technical, performance, and safety standards required for specific applications. Archimede Energia’s lithium batteries have successfully passed these rigorous evaluations, giving customers confidence that they are investing in a reliable, high-quality energy storage technology.
TYPE APPROVAL FOR MARINE BATTERY SYSTEMS: WHAT DOES IT MEAN?
Type Approval was awarded by Bureau Veritas for specific battery models from the company after passing a series of tests conducted by CevLab. This certification is particularly significant because it ensures that the batteries meet safety standards required for use in the marine sector. With this approval, Archimede Energia has become the first company in Italy to receive Bureau Veritas certification for its lithium batteries, paving the way for the use of these batteries in hybrid and fully electric vessels.
ECE R100 REGULATION: WHAT IS IT AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT
AEnerbox batteries underwent rigorous laboratory testing and passed the following tests:
- Climatic and over-temperature protection
- Drop tests
- Electromagnetic emissions (CEIN55012)
- Random vibrations (CEIN60068-2-64)
- Pollutant emissions (97/24/CE)
Archimede Energia’s lithium batteries, intended for installation in four-wheel vehicles in categories M1 and N1 (passenger and freight vehicles), passed tests conducted by CevLab and obtained approval under ECE R100 Rev 03.
ECE Regulation No. 100 sets the standards for the approval of four-wheel electric vehicles in categories M and N. Approval is carried out on the entire vehicle, including its subsystems and components, before they are introduced to the market.
The regulation also specifies the tests that must be conducted on batteries (regardless of their chemistry) used in vehicles in categories M and N. Ensuring that the battery complies with ECE R100 standards is a crucial step in obtaining approval for the entire electric vehicle, allowing it to be legally driven on roads.
WHAT TESTS ARE PERFORMED?
The tests conducted on these batteries in accordance with ECE R100 Rev 03 included:
- Vibration Test (Annex 9A): To verify battery safety under vibrations during regular vehicle operation. The test uses a sinusoidal profile with logarithmic sweep within the 7-50-7 Hz range and maximum acceleration of 10g for a total duration of 3 hours.
- Thermal Shock and Cycling Test (Annex 9B): To certify the battery’s resistance to rapid temperature changes during its lifetime. The test exposes the battery to a minimum temperature of -40°C and a maximum of +60°C, with 6 hours maintained at each temperature and the cycle repeated five times.
- Mechanical Shock (Annex 9C): To verify battery safety under inertial loads that may occur in the event of a vehicle crash. The test applies an 80 ms impulse with maximum acceleration of 28g in both longitudinal and transverse directions (for acceleration and deceleration).
- Mechanical Integrity (Annex 9D): To certify battery safety when exposed to contact stresses that may occur during a vehicle crash. The test involves compressing the battery between two plates with a load of 100 to 105 kN.
- Fire Resistance (Annex 9E): To verify battery resilience in the presence of flames from outside the vehicle (ensuring passengers have enough time to exit in case of a severe incident). During the test, the battery is exposed to direct flame (generated by gasoline combustion) for 70 seconds and indirect flame (using refractory brick shielding) for 60 seconds.
- External Short Circuit (Annex 9F): To assess battery safety in the event of a short-circuit current. This evaluates contact between the battery’s positive and negative terminals.
- Overcharge Protection (Annex 9G): To assess battery safety in the event of overcharging. The test charges the battery at a rate of C/3 or C/2 until the protective system activates to prevent overcharging.
- Overdischarge Protection (Annex 9H): To ensure battery safety when at a low charge state. The test discharges the battery at a rate of C/3 or C/2 until the protective system activates to prevent excessive discharge.
- Overtemperature Protection (Annex 9I): To assess battery safety in the case of overheating caused by charge/discharge cycles or a malfunction of the cooling system. The test continuously charges and discharges the battery to raise its internal temperature until it reaches a predefined threshold, activating the protective system to inhibit charging and/or discharging.
- Overcurrent Protection (Annex 9J): To ensure battery safety when subjected to excessive charging current. The test increases charging current beyond the manufacturer’s specified limit until the protection system activates to inhibit charging.